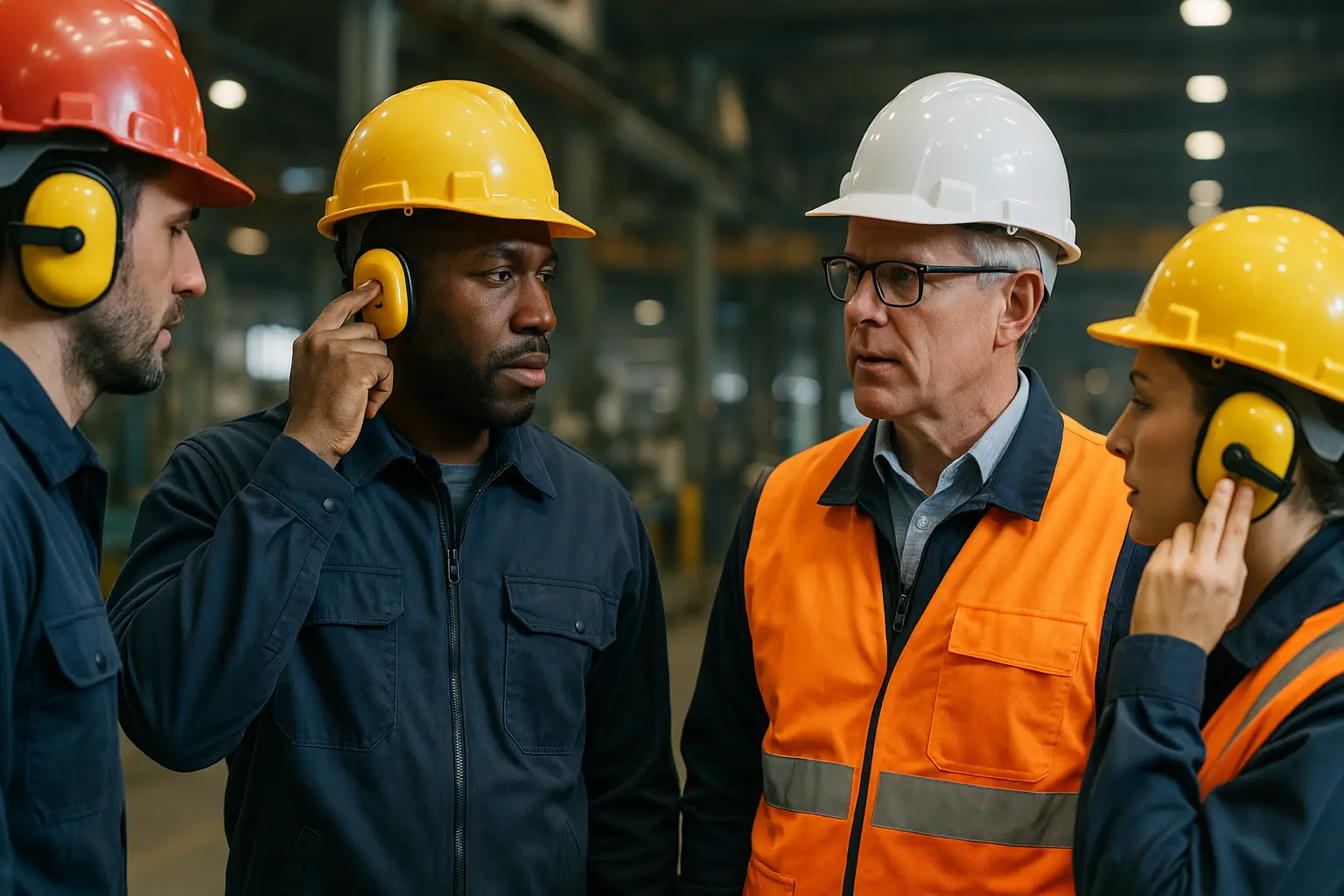
October 2025: National Protect Your Hearing Month
Every October, the United States observes National Protect Your Hearing Month, a time dedicated to raising awareness about the importance of hearing health. Our hearing plays a vital role in how we connect, communicate, and stay safe; yet it’s often taken for granted until damage occurs. Workplace noise is one of the leading causes of preventable hearing loss, affecting millions of workers across industries. In this blog, we’ll explore how noise exposure impacts hearing, the risks of noise-induced hearing loss, and practical steps you can take to protect your ears on the job.
Understanding Noise-Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL)
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL) happens when the tiny hair cells in the inner ear are damaged by loud sounds. Once these cells are destroyed, they don’t grow back, making the hearing loss permanent. Around 22 million workers in the U.S. are exposed to hazardous noise each year, according to the CDC. NIHL often develops slowly, so people may not notice the damage until it’s too late. It remains one of the most common yet 100% preventable workplace health issues. Early warning signs include ringing in the ears (tinnitus), muffled hearing, or trouble understanding speech in noisy places. Recognizing these signs early and taking protective measures can help prevent lasting damage.
How Workplace Noise Affects Hearing
Prolonged exposure to loud noise can cause serious and lasting damage to the inner ear. Inside the ear, thousands of tiny hair cells convert sound vibrations into electrical signals that the brain interprets as sound. When noise levels exceed safe limits, typically 85 decibels (dB) or higher, these hair cells can become overstimulated and eventually die, leading to permanent hearing loss.
According to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), about 22 million workers in the U.S. are exposed to potentially damaging noise each year. Industries such as construction, manufacturing, mining, agriculture, aviation, and entertainment face some of the highest risks. Even brief exposure to very loud sounds, such as machinery or power tools, can cause temporary hearing issues, while long-term exposure leads to irreversible damage.
Short-term effects of workplace noise include ringing or buzzing in the ears, ear fatigue, and temporary threshold shifts, a brief reduction in hearing sensitivity after noise exposure. Over time, this can progress to chronic tinnitus, permanent hearing loss, and even increased stress, fatigue, and reduced concentration, all of which affect overall job performance and safety. Protecting hearing isn’t just about comfort; it’s about preserving one’s long-term health and quality of life.
Occupations with Dangerous Noise Levels
Certain professions expose workers to dangerously high noise levels daily. Construction workers, factory operators, and miners often face continuous sounds between 90–100 dB, while airport ground crews and military personnel may experience noise exceeding 120 dB from engines and aircraft. Even tools like a chainsaw (110 dB) or a jackhammer (100 dB) can cause damage within minutes without protection.
Noise hazards aren’t limited to heavy industries; entertainment workers, farmers, and even office employees can be at risk. In offices, constant exposure to printers, HVAC systems, or crowded chatter can contribute to long-term ear strain and fatigue. Recognizing these hidden risks is the first step toward preventing hearing damage in any work setting.
Prevent Hearing Loss at Work with Smart Habits
Protecting your hearing doesn’t always require expensive equipment—small, consistent habits can make a big difference. By becoming more aware of your daily sound exposure and taking proactive steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of long-term damage. Here are some practical ways to safeguard your ears at work:
Take regular “quiet breaks.”
After working in a noisy environment, step away for a few minutes of silence. These quiet breaks give your ears a chance to recover from continuous sound exposure and prevent auditory fatigue over time.
Maintain a safe distance from loud sources.
Sound intensity drops quickly as you move away from the source. Whenever possible, stay a few feet back from loud machinery, speakers, or engines to reduce the impact of direct noise exposure.
Lower the volume on personal listening devices.
Listening to music or podcasts through earphones at high volume can be just as harmful as industrial noise. Follow the 60/60 rule; keep the volume under 60% and limit listening to 60 minutes at a time.
Use smartphone apps or devices to monitor noise levels.
Many free apps can measure the decibel level in your surroundings. Regularly checking noise levels helps you recognize when protection is needed, ensuring you stay within safe exposure limits throughout your workday.

How To Create A Safer Work Environment
Creating a safer sound environment at work is just as important as personal habits. Employers and employees can work together to reduce harmful noise through engineering controls, administrative measures, and proper hearing protection. These changes not only protect hearing but also improve overall comfort and productivity.
Soundproofing and acoustic panels.
Installing sound-absorbing materials, barriers, or acoustic panels can help reduce noise levels in factories, workshops, or offices. Simple improvements, like rubber mats under machines or closed doors between noisy and quiet zones, can make a big difference.
Rotating shifts to limit noise exposure time.
By alternating tasks or rotating workers between high- and low-noise areas, employers can reduce the total time each person spends in loud environments, lowering the overall risk of hearing damage.
Implementing workplace noise policies.
Clear noise control policies, such as maximum allowable noise levels and required hearing protection in specific zones, help maintain consistency and accountability across teams. Regular safety briefings also keep awareness high.
Provide and wear hearing protection devices (HPDs).
Earplugs, earmuffs, and custom-fitted protectors are essential in high-noise settings. They can reduce sound exposure by 15–30 dB when worn correctly, offering an effective first line of defense.
Encourage routine hearing tests.
Regular hearing screenings help detect early signs of hearing loss before they become permanent. Routine testing allows employees to monitor their hearing health and take corrective action promptly.
Wrap Up
Hearing is one of our most valuable senses, yet it’s often neglected in the workplace until damage has already been done. Noise-induced hearing loss is permanent but entirely preventable with the right awareness and precautions. This National Protect Your Hearing Month, take time to assess your work environment, adopt safer listening habits, and ensure protective measures are in place. Whether it’s wearing earplugs, taking quiet breaks, or encouraging company-wide hearing checks, every small step counts. Protecting your hearing today means preserving your quality of life, communication, and well-being for years to come.
Related Posts

Understanding the Future of EHS Technology

EHS Reporting: Executives vs Workers Explained